
The Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH) Division of Neuromuscular Disease and Electromyography (EMG) provides comprehensive diagnostic evaluation, consultation, and management of all neuromuscular disorders, including motor neuron disease (ALS), peripheral neuropathies, myopathies, muscular dystrophy, and myasthenia gravis.Ĭurrently, we offer comprehensive neuromuscular services, including EMG, at the main BWH campus in Boston and EMG and other diagnostic services at Brigham and Women's/Massachusetts General Health Care Center.

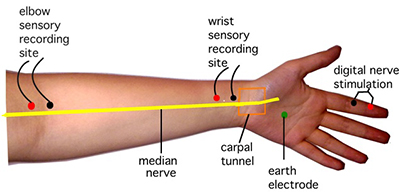
EMG Testing at Brigham and Women’s Hospital An NCV helps to differentiate a nerve disorder from a muscle disorder. The electrode will detect electrical activity and results will be displayed on a nearby monitor (oscilloscope).Ī nerve conduction velocity (NCV) test is often performed at the same time as an EMG. Once the electrode is in place, the patient will be asked to either contract their muscles or keep their muscles relaxed. What is an EMG Test?ĭuring an EMG test, a very thin needle (electrode) will be inserted through the skin and into the muscle. Electromyography (EMG) is a diagnostic test that helps detect neuromuscular abnormalities by measuring electrical activity in the muscles.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
